象牙因其堅韌的質(zhì)地和華麗的色彩而通常被用作特殊的裝飾和藝術(shù)雕刻材料。然而,由于長期掩埋于地下,古象牙經(jīng)歷了地下水腐蝕、溫度和濕度的變化以及其他環(huán)境因素導(dǎo)致其有機(jī)成分分解,結(jié)構(gòu)疏松多孔,機(jī)械強(qiáng)度下降。出土后立即脫水和風(fēng)化使其難以運(yùn)輸和保存。因此,當(dāng)務(wù)之急是要對古象牙文物進(jìn)行保存和加固,特別是要保證其原始狀態(tài)和一定的臨時加固強(qiáng)度,以便進(jìn)一步保存和運(yùn)輸。

近期,西安交通大學(xué)和玲/潘愛釗課題組針對古象牙文物臨時加固和保存等問題,設(shè)計了一種仿生和增強(qiáng)粘合的鈣基礦化水凝膠材料(Ca-gel),通過控制其組分和含量,實現(xiàn)了可控的凝膠時間和凝膠狀態(tài)。通過熒光示蹤技術(shù)研究了Ca-gel在象牙粘接界面的分布,并深入研究了其臨時粘接性能,深入評估了其長效保護(hù)效果,以實現(xiàn)對古代象牙的真實性、完整性和連續(xù)性的臨時加固和保存。Ca-gel 將有望成為臨時加固和文物保護(hù)領(lǐng)域的重要工具。該研究成果“Calcium-Based Mineralized Hydrogels for Temporary Reinforcement and Conservation of Ancient Ivory Relics”近期發(fā)表于《ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces》。
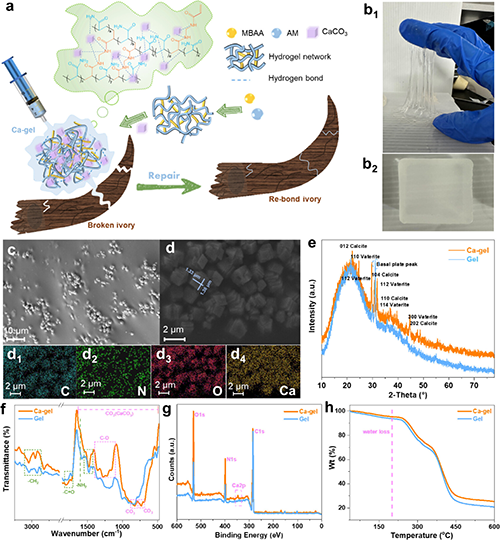
Figure 1. (a) Synthesis strategy of the Ca-gel adhesive. (b) Photographs of the developed Ca-gel adhesive. SEM (c, d) and SEM-EDS mappings (d1-d4) of Ca-gel. XRD (e), FTIR (f), XPS (g), and TG (h) of Gel (without mineralization) and Ca-gel.
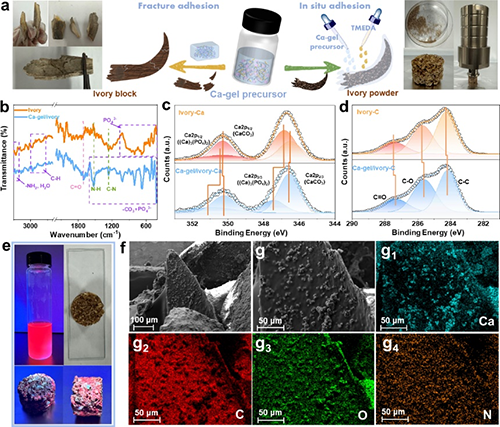
Figure 2. (a) Adhesive strategies for ancient ivory fracture samples (left, direct bonding method) and powderization (right, in situ bonding method). (b) FTIR spectra of untreated ivory and treated Ca-gel/ivory from the in situ bonding method. High-resolution XPS spectra of Ca 2p (c) and C (d) of ivory and Ca-gel/ivory from in situ bonding method. (e) Fluorescence tracer of the ancient ivory treated by Ca-gel-CdTe/ZnS from in situ bonding method. SEM (f, g) and SEM-EDS (g1-g4) of the powdered Ca-gel/ivory from the in-situ bonding method.
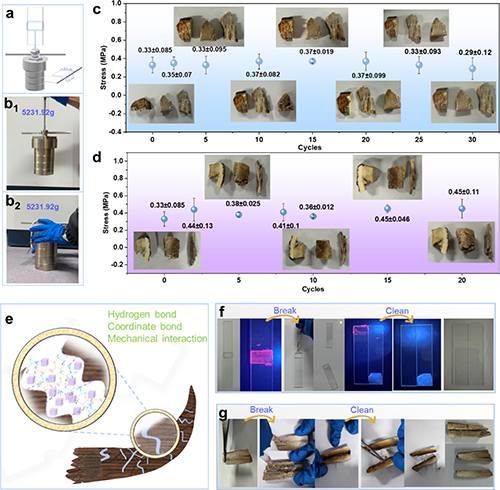
Figure 3. (a) Comparison of adhesive properties between Ca-gel and Gel, test mode diagram. (b1) Ca-gel adhesive performance test of the bonded Ca-gel/glass. (b2) Gel (without mineralization) adhesive performance test of the bonded Ca-gel/glass. (c) UVA cycles of Ca-gel/ivory from direct bonding method with standard deviation. (d) HTA cycles of Ca-gel/ivory from direct bonding method with standard deviation. (e) Schematic diagram of protection mechanism of ancient ivory by Ca-gel. (f) Fluorescence tracer technique was used to detect temporary adhesive properties and residual adhesive removal. (g) Temporary adhesive properties of Ca-gel on ancient ivory for direct bonding applications.
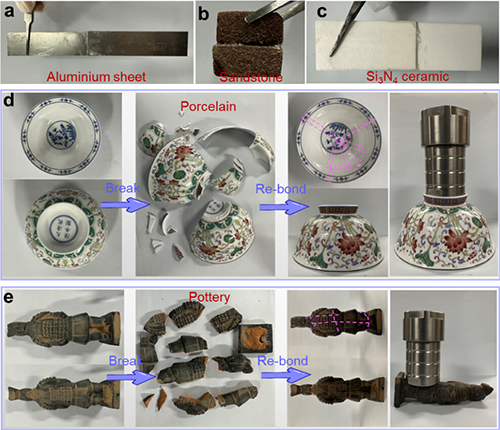

Figure 4. (a) Ca-gel-bonded aluminum sheets. (b) Ca-gel-bonded glass sheets. (c) Ca-gel-bonded silicon nitride ceramic sheets. (d) Ca-gel restorative adhesive ceramic bowl and its strength detection. (e) Ca-gel restorative adhesive pottery figurine and its strength detection from the direct bonding method.
西安交通大學(xué)化學(xué)學(xué)院博士生史承鈺為該論文的第一作者,西安交通大學(xué)化學(xué)學(xué)院和玲教授團(tuán)隊的潘愛釗副教授為該論文通訊作者,該工作還得到了甘肅省敦煌文化遺產(chǎn)保護(hù)研究中心(敦煌研究院)牛賀強(qiáng)老師的支持和幫助。該研究得到了國家重點(diǎn)研發(fā)計劃(2019YFC1520500)項目和國家自然科學(xué)基金(NSFC Grants 52172153)的資助以及西安交通大學(xué)分析測試共享中心的支持。
原文鏈接:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c14901





