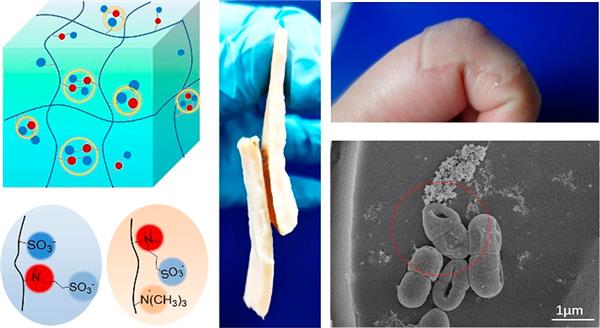
Biotissue adhesives and antibacterial materials have great potential applications in wound dressing, implantable devices, and bioelectronics. In this study, stretchable tissue adhesive hydrogels with intrinsic antibacterial properties have been demonstrated by copolymerizing zwitterionic monomers with ionic monomers. The hydrogels are stretchable to about 900% strain and show a modulus of 4–9 kPa. The zwitterionic moieties provide strong dipole–dipole interaction, electrostatic interaction, and hydrogen bonding with the skin surface, and thus show adhesion strength values of 1–4 kPa to skin. Meanwhile, the copolymerized cationic or anionic monomers break the intrinsic electrostatic stoichiometry of the zwitterionic units and thus mediate the electrostatic interactions and the adhesion strength with the surface. The stretchable hydrogels form a robust and compliant (due to low modulus and stretchability) adhesive to skin, rubber, glass, and plastics, and could be repeatedly peeled-off and readhered to the skin. Moreover, the abundant quaternary ammonium (QA) groups in the zwitterionic moieties and the added QA groups endow it outstanding antibacterial properties (>99%). These stretchable tissue adhesive antibacterial hydrogels are promising for wound dressings and implantable devices.
https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsami.0c14959