作為傳承前千年的美食,豆腐在餐桌上占據重要席位,近期研究表明,其在生物醫學應用領域也表現出巨大潛力。豆腐中含有豐富的大豆蛋白和礦物質元素,制備過程中不引入任何有毒試劑,生物安全性良好。基于豆腐工藝開發的大豆蛋白組織工程支架具備豆腐良好的生物安全性,同時具備疏松多孔的內部結構和一定的力學性能;本文同時對比了大豆蛋白化學交聯方法制備的大豆蛋白組織工程支架的性質,對它們進行了系統的研究,首次對豆腐支架在生物醫學領域中應用進行了初步探索,以期開發豆腐的在生物醫學領域的潛在價值。

Figure 1. Schematic illustration of developing tofu scaffolds and soybean protein scaffolds
近日,中山大學工學院生物醫學工程學科吳鈞課題組首次將傳統的豆腐開發成組織工程支架,并對其在生物醫學領域中的應用進行了初步探索。這是對食源性生物材料開發的又一次大膽嘗試,他們以傳統豆腐制備工藝為基礎,在不引入有毒試劑的前提下將豆腐制備成可應用于組織工程的生物支架,有望在軟組織創傷修復中發揮一定作用。本成果以Evaluation of tofu as potential tissue engineering scaffold 為題,吳鈞教授、顧志鵬副研究員為通訊作者,黃駿博士為第一作者,中山大學工學院為第一單位,于2018年1月23日發表在材料學著名期刊《Journal of Materials Chemistry B》(DOI: 10.1039/C7TB02852K) 上。
該團隊將傳統豆腐制備工藝進行簡單改良后應用于豆腐支架的開發,有效避免了有毒試劑的引入,極大的提升了材料的生物安全性;同時,對比了大豆蛋白化學交聯方法制備的大豆蛋白組織工程支架的性質。研究表明,豆腐支架與化學交聯方法制備的大豆蛋白支架具有相似的理化性能,且后期,豆腐支架表現出更佳的生物相容性,更有利于細胞的增殖和體內植入后血管的形成。
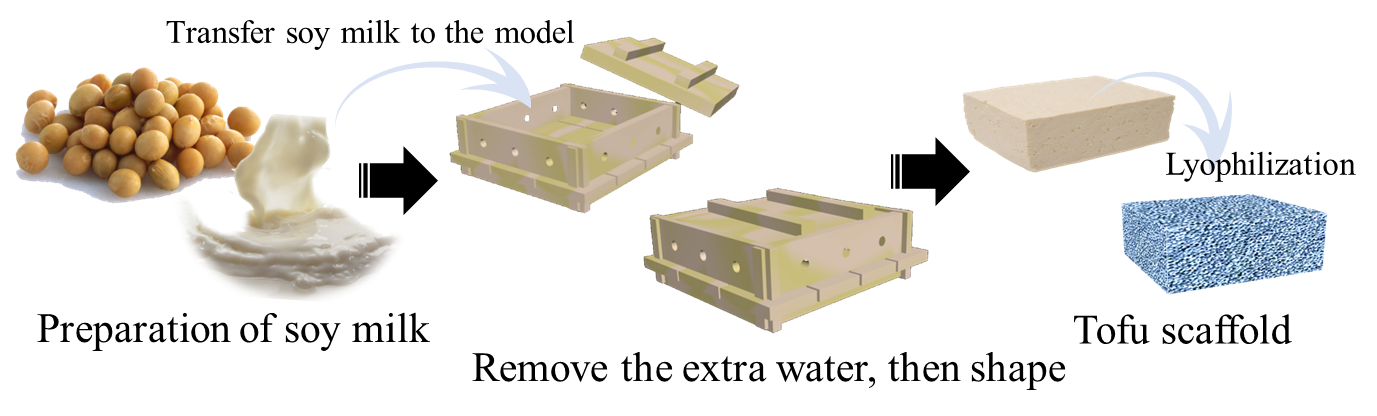
Figure 2. The simplified process of tofu scaffold preparation.
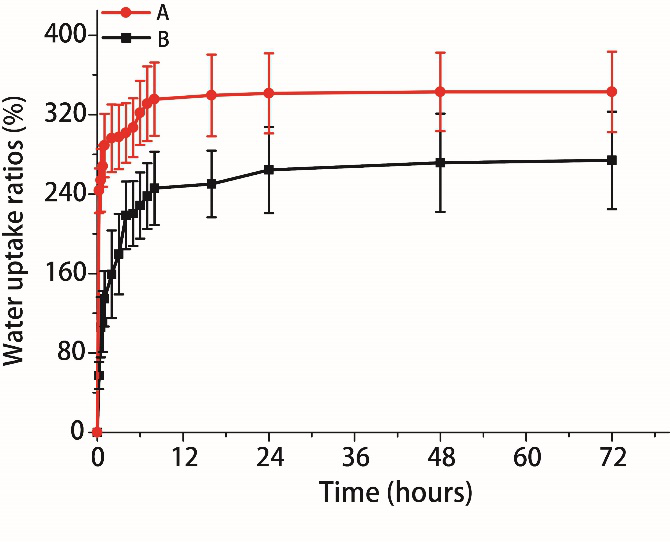
Figure 3. The water uptake ratios of tofu scaffolds and soybean protein scaffolds in 0.01 M PBS solution: (A) Tofu scaffolds. (B) Soybean protein scaffolds. Mean ± SD,n=3.

Figure 4. The stress–strain curves of tofu scaffolds and soybean protein scaffolds under wet conditions. There was no significant difference to the compression modulus of tofu scaffolds and soybean protein scaffolds. Mean ± SD, n = 3

Figure 5. The result of weight-loss ratio of soybean protein and tofu scaffold: (A) Tofu scaffold in 0.01 M PBS solution. (B) Tofu scaffold in 0.25% trypsin solution. (C) Soybean protein scaffold in 0.01 M PBS solution. (D) Soybean protein scaffold in 0.25% trypsin solution. Mean ± SD, n = 3.

Figure 6. Proliferation of NIH 3T3 cells after 7 days culture with the leaching solution of soybean protein and tofu scaffolds. *p < 0.05 (compared with the control at the same time), Mean ± SD, n = 3.

Figure 7. The morphology of 3T3 cells directly seeding in soybean protein and tofu scaffolds were analyzed by staining with rhodamine phalloidin and DAPI (A, B, C, D). Live/dead staining was carried out to verify the good biocompatibility of two scaffolds (E, F, G, H). (A&E): The morphology of 3T3 cells seeded in soybean protein scaffolds after cultivating 24 hours. (B&F): The morphology of 3T3 cells seeded in soybean protein scaffolds after cultivating 48 hours. (C&G): The morphology of 3T3 cells seeded in tofu scaffolds after cultivating 24 hours. (D&H): The morphology of 3T3 cells seeded in tofu scaffolds after cultivating 48 hours. The cell morphology is good after seeding in two types scaffolds directly, which were indicated by blue arrows. The dead cells are indicated by white arrows. Scales bar = 50 μm.

Figure 8. The results of histology evaluation implanting tofu scaffolds (A, B and C) and soybean protein scaffolds (D, E and F) after 7 days. (A & D): HE stained section of the scaffold with surrounding tissues. Tofu scaffolds part was indicated by blue arrows and good biological integration with the surrounding tissues of implantation site was observed, which represented good biocompatibility of tofu scaffolds; (B & E): Masson staining displayed obvious collagen deposition in tofu scaffold part, indicated by yellow arrows; (C & F): CD31 staining was carried out to evaluate the neovascularization. The brown spots, indicated by black arrows, represented the angiogenesis in tofu scaffolds. Many minute vessels had grown out. Scale bar = 100 μm.
本文作者以傳統豆腐制備工藝為基礎,將豆腐開發成組織工程支架。研究表明,豆腐支架與化學交聯大豆蛋白支架具有相似的理化性能;細胞實驗和動物實驗表明,豆腐支架具有良好的生物相容性,適合細胞的生長和植入體內后小血管的生成。
論文鏈接:
Evaluation of tofu as potential tissue engineering scaffold(J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, DOI: 10.1039/C7TB02852K.)
http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/tb/c7tb02852k#!divAbstract
課題組介紹:
課題組負責人吳鈞教授是中山大學工學院生物醫學工程學科博士生導師,2015年中組部青年千人計劃獲得者。于南京大學,美國紐約州立石溪大學獲得學士及碩士學位,2010于美國康奈爾大學生物醫學工程系獲博士學位;2010-2015年于美國哈佛大學醫學院及麻省理工學院Omid Farokhzad 及Robert Langer實驗室從事博士后研究。研究領域涉及可降解生物材料,藥物輸送,組織工程及納米醫學等前沿鄰域,集中于含氨基酸材料的生物醫學應用。課題組負責人已發表SCI論文超過68篇,其中第一作者及通訊作者28篇,總引用次數超過3800次。
課題組以新型生物材料,納米醫學和再生醫學為主要研究方向。納米醫學方向主要是開發新型生物可降解,生物安全的高分子功能聚合物,構建多功能高載藥納米緩控釋藥物輸送體系,重點在腫瘤治療,心血管疾病及口服給藥中的應用。再生醫學方向主要是利用新型功能材料,結合納米技術與干細胞技術,構建新型支架材料,用于組織再生及修復。誠邀有志之士加入我們,有意者可發信至郵箱:wujun29@mail.sysu.edu.cn。課題組網頁: http://wulab.bme.sysu.edu.cn/
- 北京大學邵元龍《Adv. Mater.》綜述:用于組織電子設備接口的生物材料基纖維狀植入式探針 2025-06-27
- 陳學思院士/田華雨教授/方華攀副教授 AHM:生物材料在腦部疾病中的機遇與挑戰 2025-06-08
- 武漢輕工大學朱鏈/未本美、湖北工程學院汪海波 Polym. Rev.: 膠原生物材料的最新進展 - 從提取、交聯到組織再生 2025-03-21
- 中科院遺傳發育所戴建武/趙燕南 ACS Nano:仿生脊髓纖維引導脊髓損傷后軸突再生和再髓鞘化 2023-12-15
- 浙江大學王征科課題組:多層次結構、高礦物含量支架材料在骨修復中的應用 2023-05-01
- 上海交大朱麟勇教授(國家杰青)課題組擬面向海內外招聘博士后若干名 2021-10-18
